How Do You Know if You’re Biotin Deficient?
Biotin is an essential nutrient found in many foods naturally and is also available in supplements. The water-soluble nature of biotin means your body can’t store it. Thus, to maintain adequate levels, you must consume it regularly.
Infants face the most problem with biotin deficiency since they lack the bacterium responsible for its production. In addition, egg whites contain avidin, a substance that binds biotin, so excessive consumption of egg white may lead to biotin deficiency as well.
Those who take antibiotic medicines may also be affected by the deficiency. Often, this occurs as a result of the medicine killing the bacteria that produce biotin in the intestines. People who are chronic dieters may also be deficient in biotin. In some cases, hair or weight that is lost due to biotin deficiency can be restored when the person returns to a normal diet.
Summary
- What is the Recommended Daily Biotin Intake?
- How Do You Know If You Have a Biotin Deficiency?
- What Causes a Deficiency in Biotin?
- How Can I Increase My Biotin Levels?
- Conclusion
What is the Recommended Daily Biotin Intake?
Age determines how much biotin you need each day. Here is a list of the average daily recommended amount in micrograms (mcg).
- New-borns (0-6 months) 5mcg
- Infants (7–12 months) 6 mcg
- Toddlers (1–3 years) 8 mcg
- Kids (4–8 years) 12 mcg
- Kids (9–13 years) 20 mcg
- Teenagers (14–18 years) 25 mcg
- Adults (19+ years) 30 mcg
- Pregnant women 30 mcg
- Breastfeeding women 35 mcg
How Do You Know If You Have a Biotin Deficiency?
As a deficiency, biotin is less common than others. A balanced, healthy diet tends to supply enough biotin to most people to avoid even a partial biotinidase deficiency. Natural sources of this nutrient are plentiful in many common foods, however, biotin can still be deficient in the body. The following signs and symptoms of biotin deficiency may appear if it happens:
- Irritations on the face, especially red rashes
- A scaly or dry complexion
- Dry eyes
- Frizzy hair
- Hair loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Sleeping problems or insomnia
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting
- Pain in the muscles
- Frequently upset stomach
- Lips that are cracking
Is it Common to Have a Deficiency in Biotin?
People who are susceptible to developing biotin deficiency include those who are sick or taking medications that reduce their body’s ability to absorb nutrients.
Most cases of biotin deficiency are caused by a biotinidase dysfunction (BTD). BTD is an inherited condition in which the body can no longer utilise biotin, thus causing biotin deficiency. The mutation in the BTD gene is responsible for the disease.
Biotinidase is an enzyme that the body needs to absorb biotin from food, which is made from this gene and helps with the biotin transport of nutrients. About one in 60,000 new-borns suffer from BTD. Symptoms of profound biotinidase deficiency usually develop early in a baby’s life.
What Causes a Deficiency in Biotin?
It is quite rare to have a biotin deficiency. If you have low B-7 levels, your doctor will typically look for one of these possible causes:
- Medication
You may not be able to absorb vitamins properly if you are taking certain medicines. Medications such as antibiotics and anti-seizure drugs are common causes. Furthermore, antibiotics eliminate the good bacteria in the gut that produce biotin.
- Feeding Intravenously (IV)
In patients receiving nutrition from IVs or tubes, B-7 deficiency can develop with low biotinidase activity. You may need to consume supplements until you can consume solid food again.
- Problems with the Digestive System
You may not be able to absorb food nutrients if you have chronic intestinal diseases. In addition to Crohn’s disease, colitis is also included in this group.
- Diets That Last a Long Time
You might not get a wide variety of vitamins and minerals from your diet if you practice strict eating. Maintaining or losing weight is still possible if you eat a well-balanced diet.
- Deficiency in Biotinidase
This is found in very rare genetic disorders. What happens here is you are unable to re-use biotin when you take it, where usually B-7 can be recycled by the body a couple of times before it is removed as waste. These individuals cannot recycle vitamins. Severe symptoms of this disorder often leads to an early diagnosis in order to provide biotin therapy.
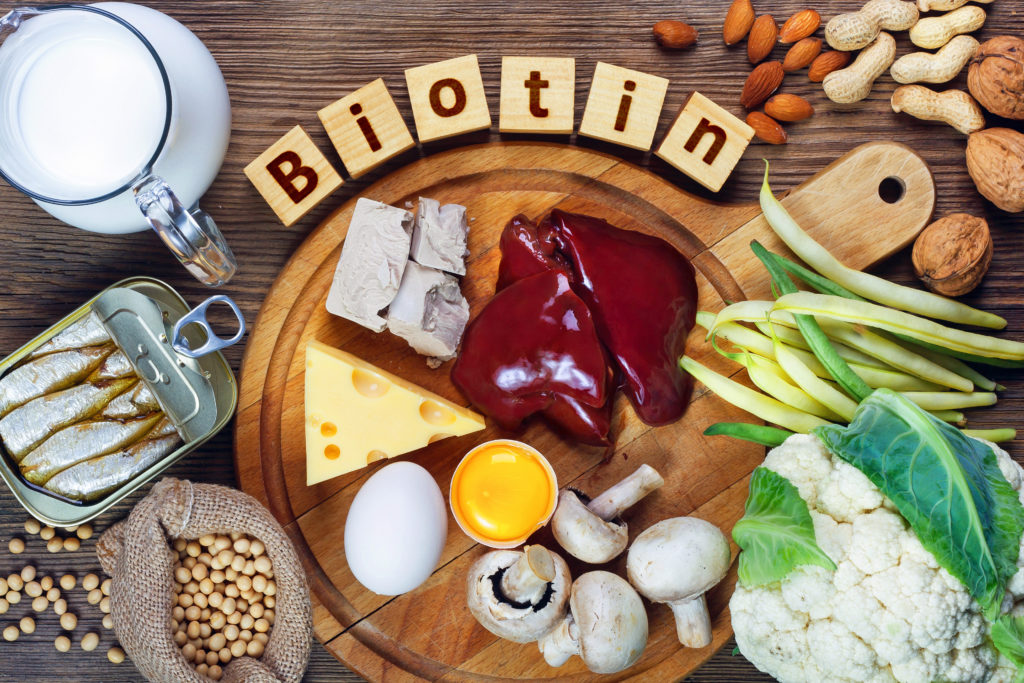

How Can I Increase My Biotin Levels?
There are two main types of treatment for a biotin deficiency – specifically foods and supplements.
1. Biotin-Rich Foods
It’s easy to meet biotin requirements daily. For adults, 30 micrograms (mcg) are recommended per day, for children 5 mcg, and expectant mothers 35 mcg per day.
Dietary sources of this vitamin are fairly easy to come by because biotin can be found in plenty of foods. Some of these include:
- Lentils, legumes, and green peas
- Sunflower seeds
- Cauliflower, carrots, and mushrooms
- Egg yolks, especially cooked eggs
- Meats from organs, such as the liver and kidney
- Dairy products such as milk, yoghurt, and cheese
- Fish
- Barley and corn, specifically whole grains
2. Biotin Supplements
Several supplements and multivitamins contain biotin. There are three amounts of biotin available on the market: 10, 50, and 100 mcg. You should seek medical advice regarding biotin supplements with your doctor before commencing.
Interactions with other medications are rare with B-7. Aside from unintended effects, this can also cause complications. Having too much biotin is also possible. Your doctor can advise you on how much to take each day.
Conclusion
It is possible to reverse biotin deficiency. Biotin supplements are prescribed to people with BTD to stop its symptoms, but they must usually take them on a long-term basis.
Supplements are not regulated by the FDA as closely as food and drugs, so people should buy from a reputable source. Taking new supplements, vitamins, herbs, or medications should also be discussed with your doctor.
In most cases, diagnosis indicates dietary changes are needed to remedy biotin deficiency, though supplements may be recommended for a limited period. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you suspect you have a biotin deficiency.